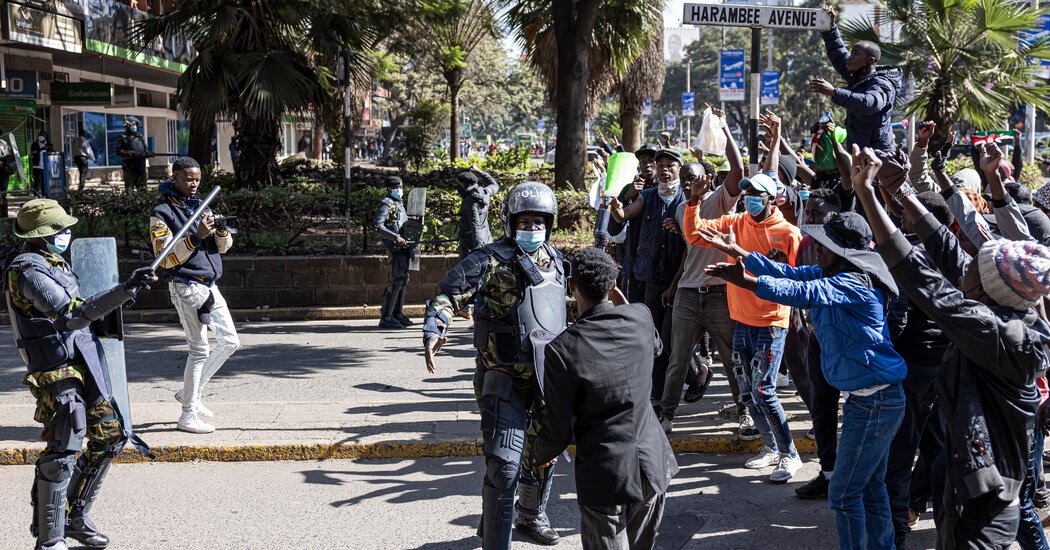[ad_1]
The prompt trigger for latest thing demonstration that clutched Kenya’s funding city on Tuesday was a boating of tax obligation boosts– extra shillings that man in the streets would certainly owe their federal government. The underlying reason, however, are the billions of bucks their federal government owes its lenders.
Kenya has the fastest expanding economic situation in Africa and a vivid service facility. However its federal government is hopeless to fend off default. The nation’s shocking $80 billion in residential and international public financial obligation represent almost three-quarters of Kenya’s whole financial result, according to a current record from the United Nations Meeting on Profession and Advancement. Rate of interest settlements alone are consuming 27 percent of the earnings accumulated.
The possibility of settlement is years away.
The financial debts that are creating anguish in Kenya can be discovered throughout Africa. Majority individuals on the continent reside in nations that invest extra on passion settlements than they do on health and wellness or education and learning.
” The children in this generation that will not have education and learning today are mosting likely to be marked permanently,” claimed Joseph Stiglitz, a previous principal financial expert at the Globe Financial institution. He kept in mind that there had actually been boosting proof that “nations that experience a dilemma do not recuperate– perhaps ever before– to where they would certainly have been.”
The international financial obligation situation is the reasonably dull tag utilized to explain the ruthless loopholes of unsustainable loaning and bailouts that have lengthy ensnared establishing countries. This newest cycle– thought about to be the most awful on document– was sped up by occasions much past any type of solitary nation’s control.
The lethal coronavirus pandemic shuttered currently vulnerable economic climates. The unexpected demand to give vaccinations, healthcare, safety clothes to medical facility employees and aids to individuals not able to manage food or food preparation oil more diminished federal government checking account.
A battle in between Russia and Ukraine in addition to assents enforced by the USA and its allies triggered international food and power rates to rise. The most affluent nations after that confined spiraling rising cost of living by elevating rates of interest, creating financial obligation settlements to swell.
In addition to those problems, current floodings in Kenya damaged facilities and farming land and displaced countless individuals.
M. Ayhan Kose, replacement principal financial expert at the Globe Financial institution, claimed “40 percent of establishing nations, somehow, are at risk to a financial obligation situation.”
Finding a remedy to the present financial obligation catch that bad and middle-income countries locate themselves in is more difficult than ever before.
Hundreds of lenders have actually changed the handful of huge financial institutions in position fresh York and London that utilized to manage most nation’s international financial obligation. Among one of the most substantial brand-new gamers is China, which has actually been lending billions of bucks to federal governments in Africa and all over the world.
Beginning again a years back, China shouldered its means right into the rankings of significant loan providers to arising countries and the dimension of its profile currently measures up to the International Monetary Fund and the Globe Financial institution.
Of the $37.4 billion in international financial obligation that Kenya owed at the end of 2022, at the very least $6.7 billion was owed to China, according to the I.M.F.
To prevent default, nations like Kenya are forced to obtain much more cash, just to locate that their overall financial obligation concern expands also larger. And the larger the financial obligation, the much less likely loan providers are to use extra funding.
China has actually cut down its loaning in the previous a number of years, after wrapping up that it was taking a lot of dangers by offering to low-income nations. It has actually accumulated on previous fundings and has actually provided less brand-new fundings.
It is not the only gamer to draw back. Japan and France along with huge business financial institutions in Italy, Germany and Britain have actually additionally cut their direct exposure.
It took Zambia 4 years to negotiate with its lenders after it initially skipped. Ghana, after back-pedaling billions of bucks of financial obligation in 2015, got to a contract just today with exclusive lenders to reorganize $13 billion well worth of fundings. And Ethiopia is having a hard time to exercise a restructuring arrangement.
In February, Kenya paid greater than 10 percent on global bonds to have the money to cover a $2 billion Eurobond repayment coming due this month.
The Globe Financial Institution, the I.M.F. and the African Advancement Financial institution have actually all used lifelines and boosted their loaning to Kenya to fill up the space when nobody else would certainly. However they, subsequently, desire the federal government to take actions, like elevating tax obligations, to locate a tougher monetary ground.
A contract this month in between Kenya and the I.M.F. to give extra cash cautioned of a “substantial shortage in taxation” and a weakening financial expectation.
In May, William Ruto, the nation’s head of state, claimed he was positive that Kenyans would ultimately happen to sustaining his activities. “I have actually been really honest that I can not remain to obtain cash to pay incomes,” he claimed in a meeting. “And I have actually discussed to individuals of Kenya that we have a selection either to obtain cash or to gather our very own tax obligations.”
This month, Pope Francis assembled a conference at the Vatican and required financial obligation mercy and a reconsidering of the globe’s monetary style to stop financial obligation dilemmas such as the one stunning Kenya.
Uncontrollable financial obligation, he claimed, burglarizes “numerous individuals of the opportunity of a suitable future.”
Declan Walsh and Ruth Maclean added reporting.
[ad_2]
Source link .